Contextualization of Windows VMs
OpenNebula uses a method called contextualization to send information to the VM at boot time. Information is collected in the Template and is essential to configure the VM.
The VM template has a section called "Context" where you can automate different configuration aspects.
The Context section has 3 parts:
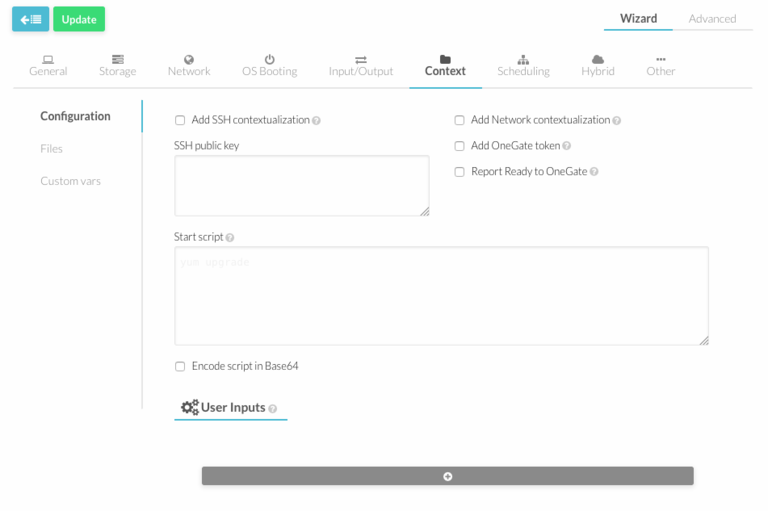
Configuration
This is the most basic context configuration provided by OpenNebula, where you can:
- Enable Network contextualization. The VM will be configured with the information added in the network section or in Custom Var section of the template.
- Enable SSH contextualization. Ssh service will be enabled.
- Add SSH public keys. Keys will be added to USERNAME authorized_keys file (See custom section) or to root in case USERNAME is not set.
- START_SCRIPT - Script which is executed when the machine starts up. It can contain either shell script or Shebang. For example START_SCRIPT="yum upgrade".
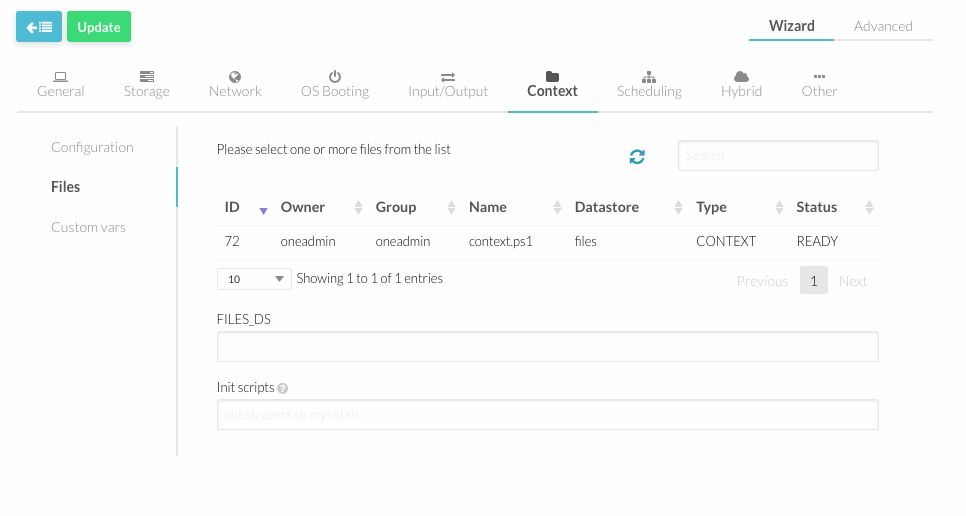
Files
You can select files you want to include from the list and they will be automatically added in FILES_DS attribute.
Also you can define a space-separated list of scripts that will run at boot, using INIT_SCRIPTS attribute.
Files can be added in "Files" section in the left menu under "Images".
Make sure that context.ps1 has been selected.
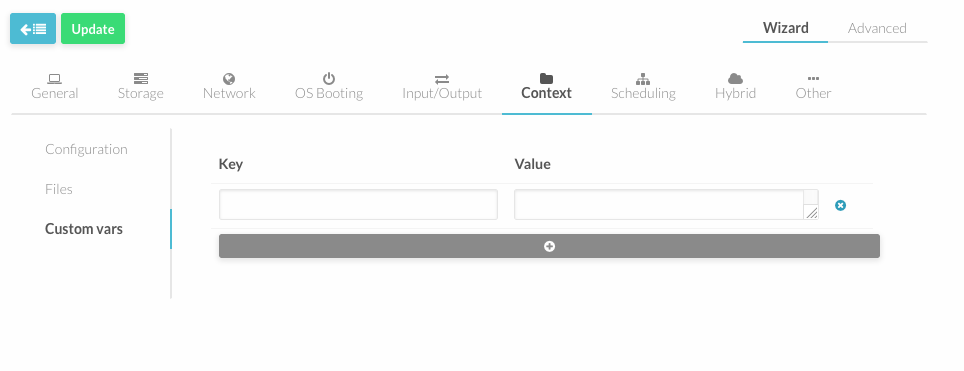
Custom Vars
In this section you can setup a more advanced contextualization, the attributes available are:
- VARIABLE - Variables that store values related to this virtual machine or others . The name of the variable is arbitrary (in the example, we use hostname).
- SET_HOSTNAME - This parameter value will be the hostname of the VM.
- ETHx_MAC - Used to find the correct interface
- ETHx_IP - IPv4 address for the interface
- ETHx_NETWORK - Network address of the interface
- ETHx_MASK - Network mask
- ETHx_GATEWAY - Default IPv4 gateway for the interface
- ETHx_DNS - DNS for the network
- USERNAME - User to be created in the guest OS. If any password attribute is defined (see below) it will change this user (defaults to root).
- PASSWORD - Password to be set for the user USERNAME. This parameter is not recommended, use PASSWORD_BASE64 instead.